CFD, short for Contract for Difference, is a type of derivative trading that allows you to speculate on the price movements of financial markets—such as stocks, indices, commodities, and currencies—without owning the underlying assets.
CFD trading is popular due to its high leverage, ease of access, and relatively low capital requirements. It gives traders the opportunity to profit from both rising and falling markets. However, while the potential for returns is attractive, it’s equally important to understand the risks and responsibilities involved.
In this guide, we’ll walk you through:
- The key features of CFD trading
- The benefits and risks
- What you need to know before you start trading CFDs
Key Features of CFD Trading
CFD trading allows traders to speculate on the price movements of various financial instruments—such as stocks, indices, commodities, currencies, and cryptocurrencies—without actually owning the underlying asset.
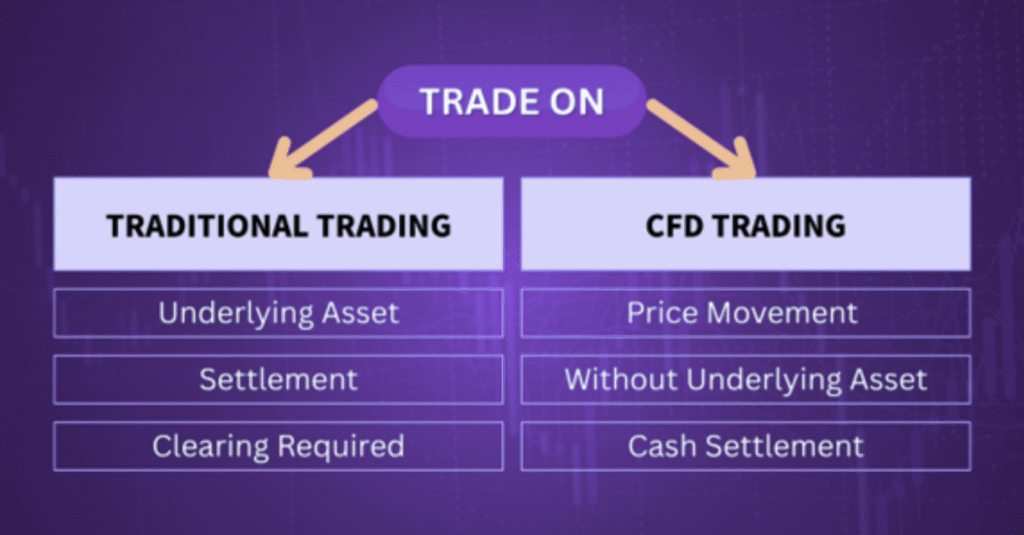
One of the defining features of CFD trading, as suggested by its name “Contract for Difference,” lies in its settlement method: the transaction is settled based on the difference between the opening and closing prices of the underlying instrument, rather than through the exchange of physical goods or securities.
The concept of CFD trading originated in the early 1990s in London. It was initially created as a cost-effective way for institutional investors and hedge funds to avoid the stamp duty levied during the physical delivery of shares.
Throughout the 2000s and 2010s, CFDs grew in popularity across Europe, Australia, and parts of Asia. Today, they remain a core offering of many online brokers, providing retail traders with access to a wide range of global markets.
How CFD Trading Works
Simply put, CFD trading involves entering into a contract between a trader and a broker to exchange the difference in the price of a financial instrument from the time the trade is opened and when it is closed.
Unlike traditional trading, where you buy and own the underlying asset, CFD traders simply speculate on price movements—either upward or downward—without owning the underlying asset.
Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
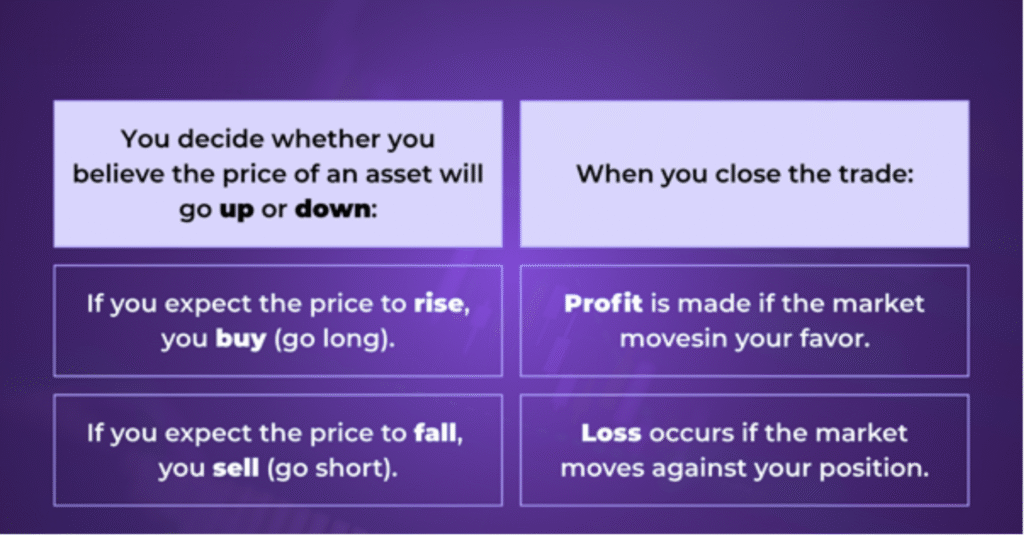
The amount of profit or loss is determined by the difference between the opening and closing price, multiplied by the number of CFD contract size or units.
Example:
- You buy 100 CFDs of Stock X at $50 (expecting it to rise).
- Later, you close the position at $55.
- Your profit is: (55 – 50) × 100 = $500 (excluding fees).
- If the price had dropped to $45 instead, your loss would be $500.
Leverage and Margin
One of the most popular reasons why traders choose CFDs is the ability to use leverage. CFDs are traded on margin, which means you only need to deposit a small portion of the full trade value—called the initial margin—to open a position.
What is Leverage?
Leverage allows you to control a larger trade with a smaller amount of capital. For example, a 10:1 leverage ratio means you only need to put up 10% of the trade value. If you’re trading a $10,000 position, you only need $1,000 in your account.
What is Margin?
Margin is the amount of money a trader must deposit with their broker to open and maintain a leveraged position. It is not a fee, but rather a security deposit to cover the potential losses.
Understanding Margin and Leverage Matters
Using margin lets you trade with more flexibility, but it also increases your exposure to market risk. If the market moves against your position, losses can accumulate quickly—and may even exceed your initial deposit if not managed properly.
That’s why it’s important to:
- Monitor your account balance and free margin regularly
- Use risk management tools like stop-loss orders
- Avoid overleveraging your trades
Benefits and Risks of CFD Trading
If you’re new to CFD trading, it’s important to understand both the advantages and risks before diving in. While CFD trading can offer exciting opportunities and flexibility, it also involves a high level of risk due to leverage and market volatility. Here’s a simple breakdown of the key pros and cons of trading CFDs.
Key benefits of CFD trading
CFD trading offers a range of benefits that make it attractive to both beginners and experienced traders:
- Access to Global Financial Markets
Trade CFDs on stocks, indices, forex, commodities, and cryptocurrencies—all from a single trading platform. - Profit from Bull or Bear Markets
You can go long (buy) when you expect prices to rise or go short (sell) when you think prices will fall. This gives you the flexibility to profit in any market condition. - Leverage Trading
Control larger trade positions with a small deposit. Leverage amplifies both gains and losses, making it a powerful but risky tool. - Low Entry Requirements
Many brokers allow you to start trading with a relatively small capital, making it more accessible to retail traders.
Risk to Aware in CFD Trading
While CFDs provide flexibility, they also come with significant risks that every trader should consider:
- High Risk from Leverage
Leverage can magnify your profits—but also your losses. A small market move against your position could result in substantial losses. - Margin Calls
If your account balance falls below the required margin level, your broker may ask you to deposit more funds or automatically close your trades. - Costs and Overnight Fees
Holding positions overnight often incurs swap or financing fees. These costs can add up, especially for longer-term positions. - Emotional Trading
The fast pace of CFD trading can lead to emotional decisions, overtrading, or taking on too much risk without a proper strategy.
CFD trading offers flexibility, low entry costs, and access to global markets—but it’s not without risks. To succeed, traders must use risk management tools, understand leverage, and choose regulated brokers. Always start with a demo account or trade small amounts while building your experience.
Regulation and Broker Considerations
When trading CFDs, choosing the right broker is just as important as understanding the market. Since CFDs are complex and high-risk financial products, working with a regulated and trustworthy broker is crucial for protecting your funds and trading experience.
Why Regulation Matters
A regulated broker must follow strict rules set by financial authorities, which helps protect traders from fraud, unfair practices, and poor fund management. Look for brokers regulated by well-known financial regulators, such as:
- ASIC – Australian Securities and Investments Commission
- FCA – Financial Conduct Authority (UK)
- ESMA – European Securites and Markets Authority
- CySEC – Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission
How to Choose a CFD Broker
Here are key factors to consider when choosing a CFD broker:
- Regulatory Status: Make sure the broker is licensed by a respected authority.
- Platform Usability: Choose a trading platform that is user-friendly and reliable.
- Spreads and Fees: Compare transaction costs, spreads, overnight swap rates, and commission charges.
- Available Markets: Ensure the broker offers access to the CFD instruments you’re interested in—stocks, forex, commodities, crypto, etc.
- Customer Support: Look for responsive, multilingual support, especially if you’re a beginner.
- Deposit and Withdrawal Options: Check for secure and convenient payment methods with low fees.

